Video
The Video element embeds video content on your page using the HTML <video> tag. It provides a complete video player with customizable controls, poster images, and multiple source options for cross-browser compatibility and responsive delivery.
This is a container element that can be changed into any HTML tag. Learn more about element types →
This element creates multiple nested HTML elements to provide advanced and flexible functionality. Learn more →
Video Element Settings
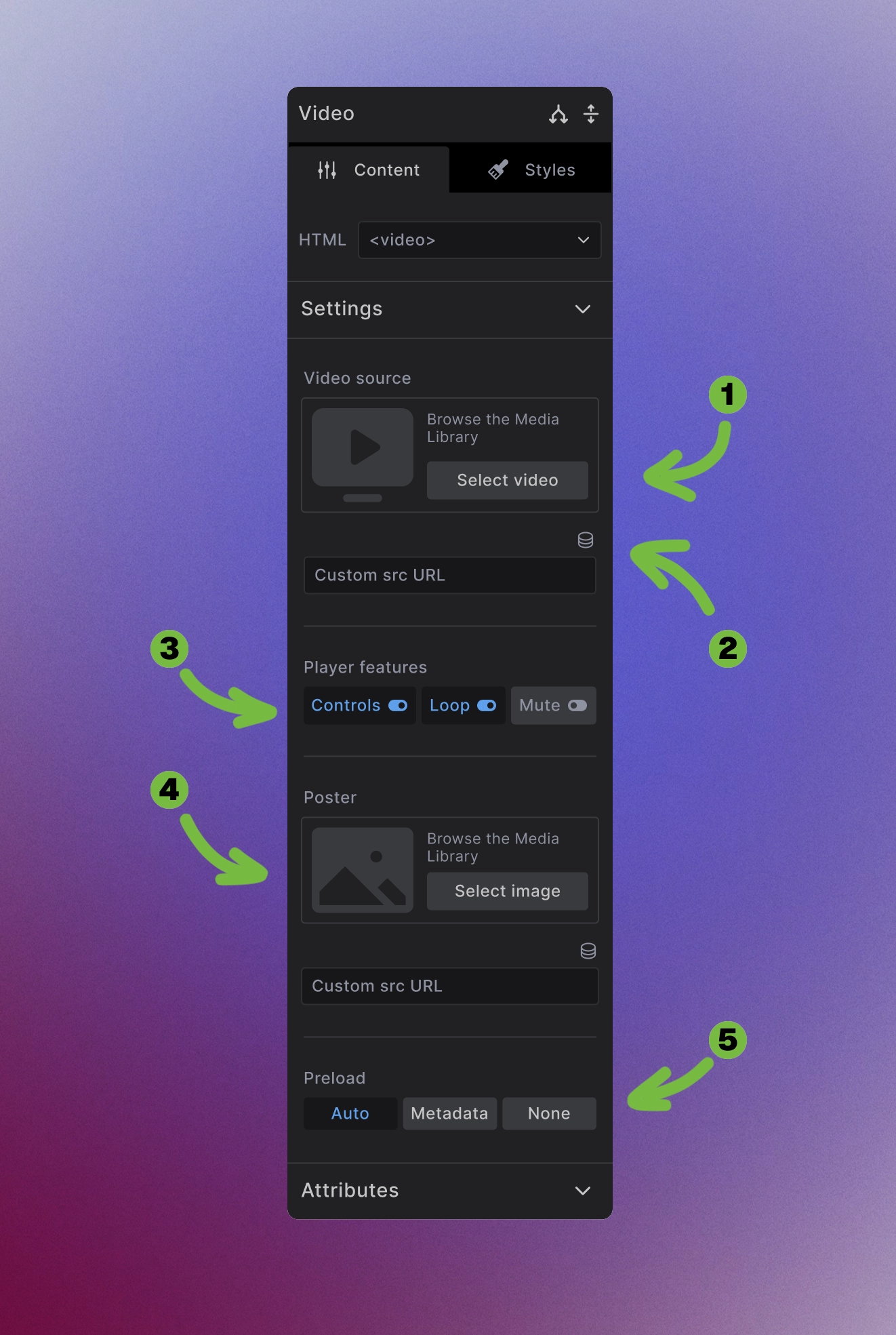
The Video element provides comprehensive video configuration options:
-
Media Library Video Source: Select video files from the media library or upload new videos.
-
Advanced Audio Sources: Use dynamic data source or Enter direct URLs for external video sources or CDN-hosted videos
-
Player features: Control video behavior with toggles for:
- Controls - Show/hide video player controls
- Loop - Automatically restart video when it ends
- Mute - Start video with audio muted
-
Poster image: Select a preview image that displays before the video plays, enhancing the user experience and providing visual context.
-
Preload behavior: Control how much video data loads initially:
- Auto - Load the entire video
- Metadata - Load only video metadata (duration, dimensions)
- None - Don't preload anything
Video Source Management
- Format compatibility: Provide multiple video formats for maximum browser support:
- Responsive delivery: Combine with Source elements for adaptive video delivery based on screen size or connection speed.
<video controls poster="preview.jpg">
<source src="video.webm" type="video/webm">
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
Your browser doesn't support video playback.
</video>
Player Features Configuration
Controls toggle: Enable or disable the built-in video player interface:
<!-- With controls -->
<video controls src="video.mp4"></video>
<!-- Without controls (often used with custom JavaScript) -->
<video src="video.mp4"></video>
Autoplay and loop: Control playback behavior:
<!-- Loop video continuously -->
<video controls loop src="video.mp4"></video>
<!-- Start muted (required for autoplay in most browsers) -->
<video controls muted src="video.mp4"></video>
Mute option: Starting videos muted is often required for autoplay functionality and improves user experience.
Poster Image Optimization
Visual preview: Poster images provide immediate visual context and improve perceived loading performance:
<video controls poster="video-preview.jpg" src="video.mp4">
Your browser doesn't support video playback.
</video>
Best practices for posters:
- Use representative frames from the video
- Optimize image size for faster loading
- Match aspect ratio of the video
- Provide meaningful visual context
Preload Strategies
Auto preloading: Downloads the entire video immediately - use sparingly to avoid bandwidth waste:
<video controls preload="auto" src="video.mp4"></video>
Metadata preloading: Loads video information without downloading content - good balance of UX and performance:
<video controls preload="metadata" src="video.mp4"></video>
No preloading: Minimal initial load - best for mobile or bandwidth-conscious situations:
<video controls preload="none" src="video.mp4"></video>
Accessibility Considerations
Captions and subtitles: Include track elements for accessible video content:
<video controls>
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<track kind="captions" src="captions.vtt" srclang="en" label="English">
<track kind="subtitles" src="subtitles.vtt" srclang="es" label="Spanish">
</video>
- Keyboard navigation: Native video controls are keyboard accessible by default.
- Screen reader support: Provide descriptive text and ensure video content is announced properly.
Performance Best Practices
- Optimize video files: Compress videos appropriately for web delivery while maintaining acceptable quality.
- Choose appropriate preload settings: Balance user experience with bandwidth consumption based on your audience.
- Responsive considerations: Consider different video qualities for different screen sizes and connection speeds.
- Loading strategy: Place videos strategically to avoid impacting initial page load performance.
Browser Compatibility
- Multiple formats: Provide fallback formats for comprehensive browser support:
- Progressive enhancement: Always include fallback content for browsers without video support.
<video controls poster="preview.jpg">
<source src="video.webm" type="video/webm">
<source src="video.mp4" type="video/mp4">
<source src="video.ogv" type="video/ogg">
<p>Your browser doesn't support video playback.
<a href="video.mp4">Download the video</a> instead.</p>
</video>
Next steps: